How much does the Prototype cost?
Types of prototypes of products
How to choose the right type of prototype
Overview of the main types of prototypes used in product development, explained according to their role within the innovation cycle and the objectives pursued at each stage of the process.
Complete guide to types of prototypes
There are two main groups of prototypes: prototypes based on innovation process priorities, and prototype types based on the target industry.
Types of prototypes based on process priorities
Idea validation
Defining the business opportunity. These prototypes need to be very lightweight; the goal is to prove there's a real, unsolved problem in the market.
Technical validation
The aim is to remove the main technical uncertainties surrounding the invention. These are slightly more complex types of prototypes that require some research.
Cost optimization
These types of prototypes are very close to the final product. They aim to prove the product's industrial viability.
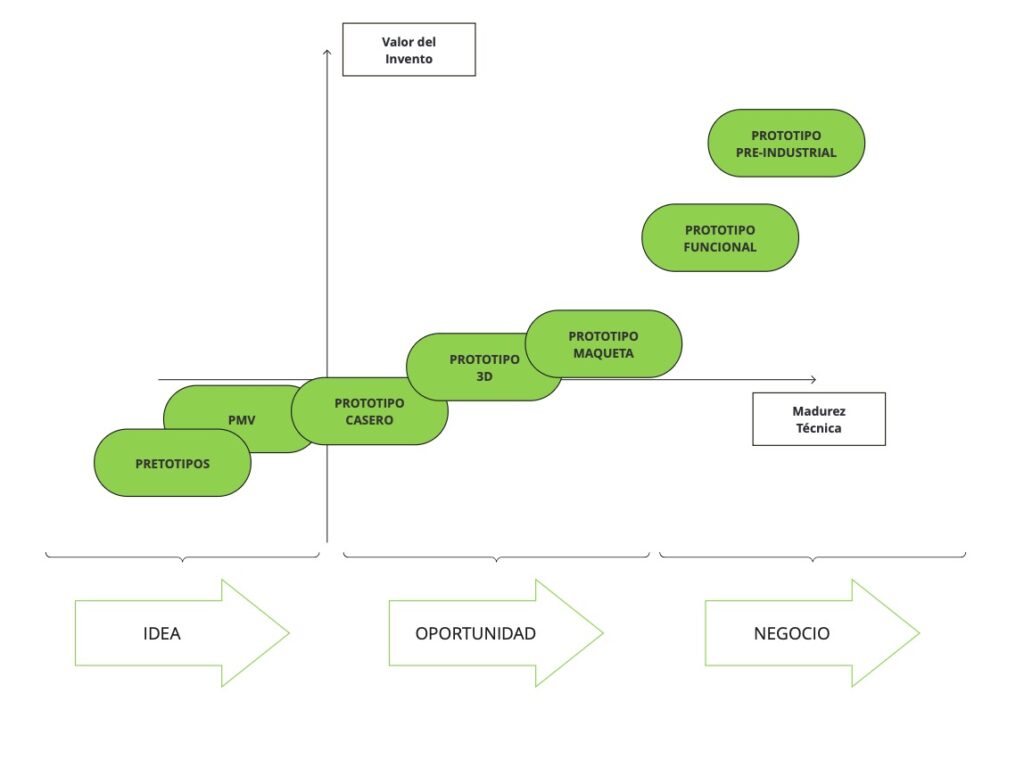
Visual map of the most common types of prototypes
Prototype Type 1: Minimum Viable Products (MVPs)
The minimum viable prototype is not a representative version of the idea. The sole purpose of the minimum viable product prototype is to demonstrate that the problem identified by the inventor exists in other people and is not unique to them. The minimum viable product can be a video, a landing page, or another useful medium to describe the value proposition of the idea and measure the reaction of users or potential customers.
Examples of successful MVPs
Dropbox – The founding team of the technology platform Dropbox, after a resounding and outright failure in a product development process, learned the importance of measuring customer behavior before investing tens of thousands of dollars. Drawing from this experience, they decided to launch a video explaining the value proposition of the future platform, describing the idea, and outlining how the platform would solve the problem of file inaccessibility due to various situations. All of this, before starting the development of an innovative software product.
The minimum viable product prototype, in this case in video format, allowed the founders to measure a set of indicators revealing the connection between the innovative solution or product idea they intended to develop and the interests of their potential customers.
Prototype Type 2: The Pretotype
The product preprototype is nothing more than an experiment that allows simulating in a natural environment the situation in which users face certain problems, in order to "simulatedly" make them see and experience the solution. In this way, the behavior of users will be measured through a specific simulation of the solution intended to be conveyed with the future prototype or innovative product.
The main difference between a product pretotype and a minimum viable product is that in the case of the minimum viable product, the solution can be conveyed or communicated by any means to measure the behavior or reaction of potential customers. In contrast, with a product pretotype, the value proposition is communicated with the customer nearby, and the functioning of a product similar to the idea intended to be developed as an innovative invention is simulated.
Objectives of the pre-prototype
The objective of a preprototype is to measure the reaction of customers to a simulation of responding to a specific problem. With these measurements, we can not only determine that the problem to be solved exists, but also that the form or solution path we intend to develop through a future prototype or product is accepted by potential customers.
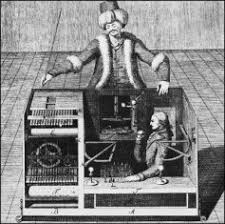
Examples of the pretotype typology
IBM presented at a fair a system or machine for its famous "Voice to Text" experiment. The main objective for IBM was to demonstrate whether customers at the time were willing to pay or at least showed interest in a machine capable of converting any voice dictation into text, also instantly generating
To validate customer interest before developing a new prototype, IBM brought a large device, with a human inside, who typed in real-time the content received from the voice of the participants at the fair. In this way, the device, with a human inside, was sufficient to demonstrate the interest generated by the solution in the customers.
Prototype Type 3: Homemade Prototypes
A home prototype is the handmade version of the product often developed by inventors to demonstrate that their invention idea works and solves a real problem. Home prototypes are usually made with existing materials, manually adapted by the inventor to form a less professional prototype but very important, as it is the first approximation to the prototype's functions. Although the home prototype is important, it should not be confused with the economic viability and technical feasibility of a prototype, these aspects must be professionally validated and optimized by product design and development experts.
What homemade prototypes can I manufacture?
Los inventores pueden fabricar diferentes versiones de prototipos caseros. Los prototipos caseros no están preparados para aproximarse a la industria, ya que sus componentes no suelen ser óptimos para fabricar en serie el producto. Es posible fabricar prototipos caseros de electrodomésticos y sobre todo de productos mecánicos.
What is a homemade prototype used for?
Homemade prototypes are very useful for conveying the functional requirements of the prototype. By analyzing the characteristics of the homemade prototypes of an invention, the main objectives of the innovative product are defined. Homemade prototypes allow the inventor to express with greater certainty and specificity the objectives they intend to achieve in the product creation cycle.
Prototype Type 4: 3D Prototypes
La definición de prototipo 3d es un diseño conceptual de la idea. Utilizando herramientas de diseño 3d y desarrollo mecánico, es posible crear un concepto muy realista del prototipo en 3d. El diseño 3d de un prototipo no garantiza que el prototipo funcione ni tampoco que sus componentes y mecanismos sean los definitivos. En el proceso de creación de un prototipo se debe utilizar el diseño 3d del producto como guía pero nunca como herramienta de restricción. Intentar copiar exactamente el diseño de prototipo 3d puede atentar contra las posibilidades de mejora del prototipo en el proceso de fabricación así como en el proyecto de ingeniería básica de un prototipo.
Objectives of the 3D prototype
A 3D prototype offers a realistic view of the concept of an innovative product intended for development. The ability to design a 3D prototype aims to measure the reaction and behavior of customers when visualizing the product before it exists. The 3D prototype enables inventors and prototype design companies to learn from customer feedback to improve the product's ergonomics and analyze the expectations of potential customers for the future innovative product intended for development. It is important to design more than one 3D prototype; this way, we will present customers with different versions of the 3D prototype to compare their reactions and feedback, especially regarding the anticipated ergonomics of an innovative product.
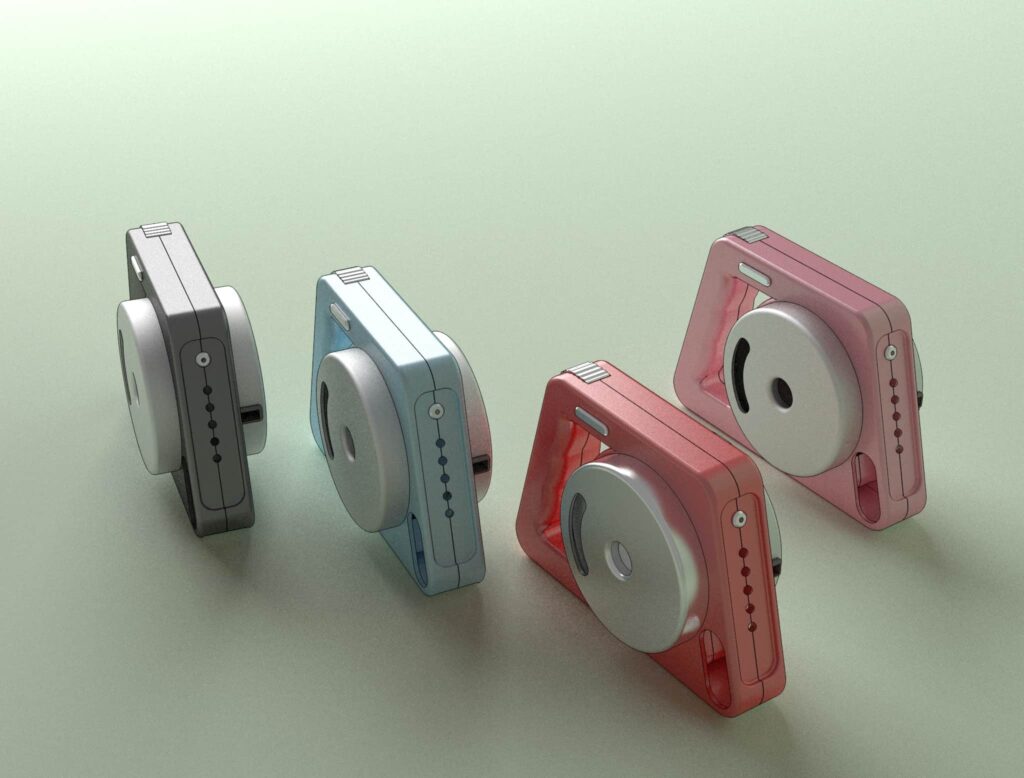
Example of a 3D prototype
Our team of 3D prototype design and functional prototype manufacturing work hand in hand to connect these stages, keeping in mind that before manufacturing a prototype, it is crucial to test the 3D prototype to assess customer expectations.
For example, currently, we are designing a prototype of a leash useful for walking pets. This leash includes a water reservoir, liquid dispensing system, and a bag dispenser for picking up pet waste. Bringing together all these functional subsystems in a prototype is a challenge in terms of product ergonomics, as the prototype's shape<span style="
Below you can see an example of a 3D prototype that will likely undergo significant improvements and changes based on the initial feedback from future customers.
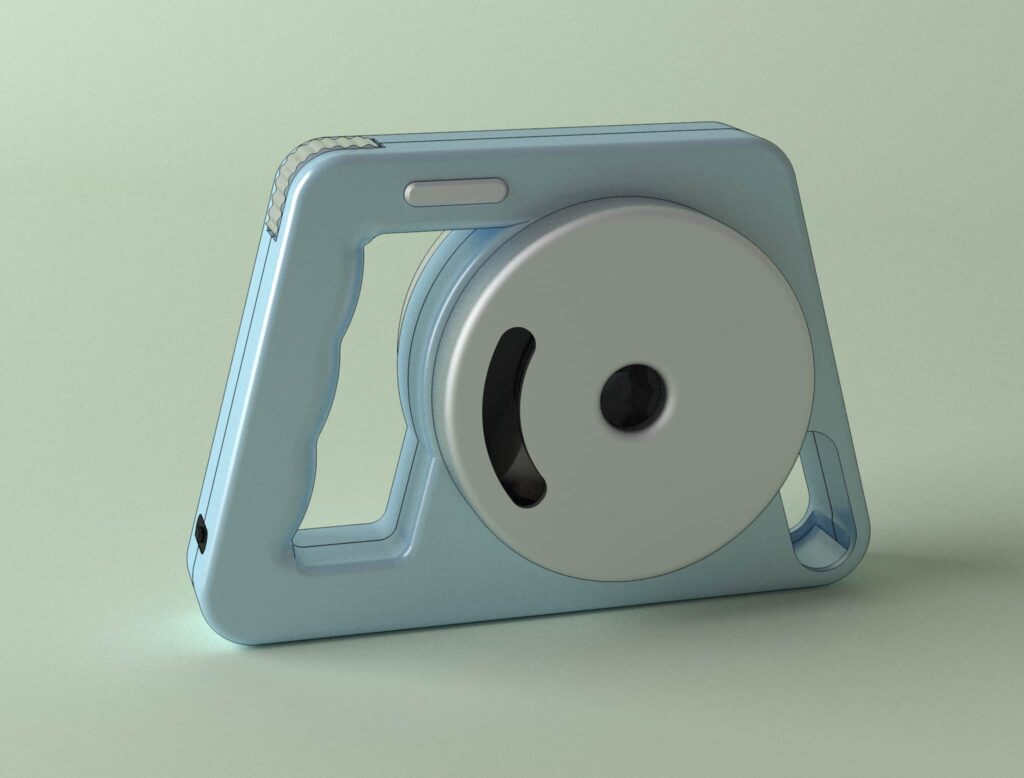
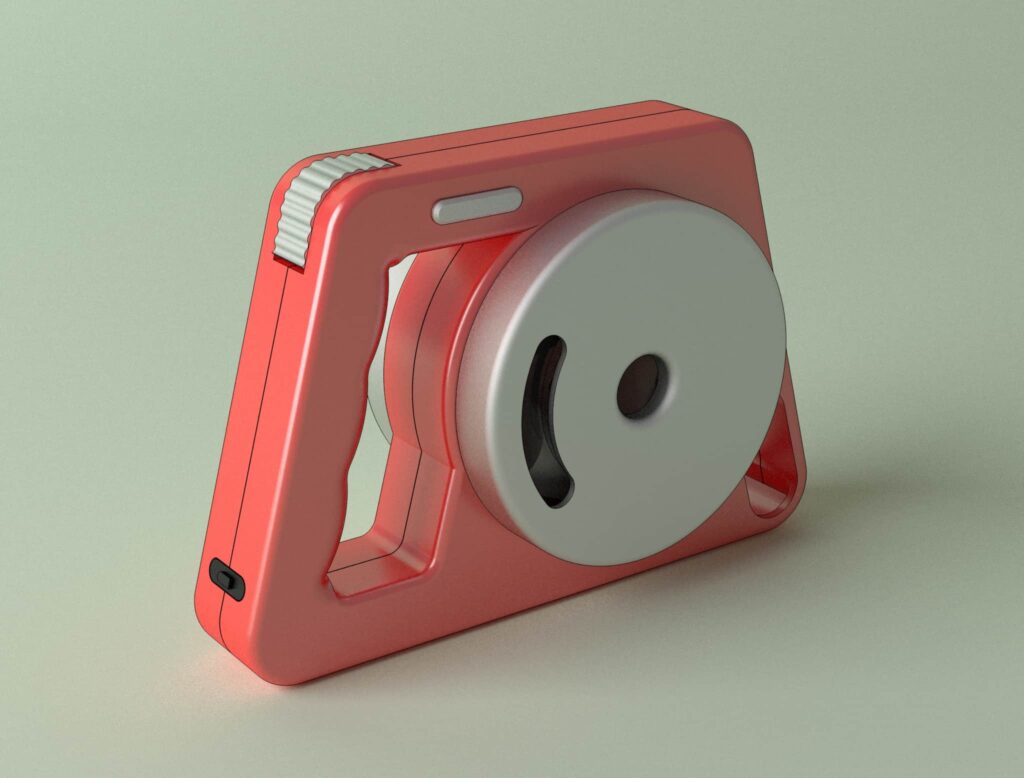


Prototype Type 5: Product Models
The mockup prototype or product mockup is not the functional prototype. It is a physical representation of the prototype's shape, allowing future customers and the inventor themselves to touch and handle the prototype before integrating the mechanisms or subsystems that enable the functionality of a prototype.
With the mockup prototype, customers can determine the ergonomics of the product, analyze the feasibility based on the size, weight of the prototype, and potential costs associated with manufacturing the outer casings of the prototype.
The product mockup or mockup prototype does not provide insights into the manufacturing costs of a product; this is an objective associated with pre-industrial prototypes.
Product mockups can be constructed using 3D printing techniques, laser cutting machines, and other modern tools that help keep the cost of a product mockup from becoming too excessive. A product mockup must be inexpensive and easily transformable by necessity, as it is an initial prototype that is highly experimental, aiming solely to reach a consensus between the technical viability of the prototype, the anticipated economic viability of a prototype, and the interests and ergonomics of product use.
Objectives of the Mockup Prototype
The product mockup or prototype mockup is useful for determining the ergonomics of the product, simulating usage examples. Similar to the 3D prototype case, it's crucial to manufacture multiple prototype mockups with different shapes and colors. This way, not only can the reaction of future clients be measured, but their feedback regarding the potential use of the different product mockups can also be compared.
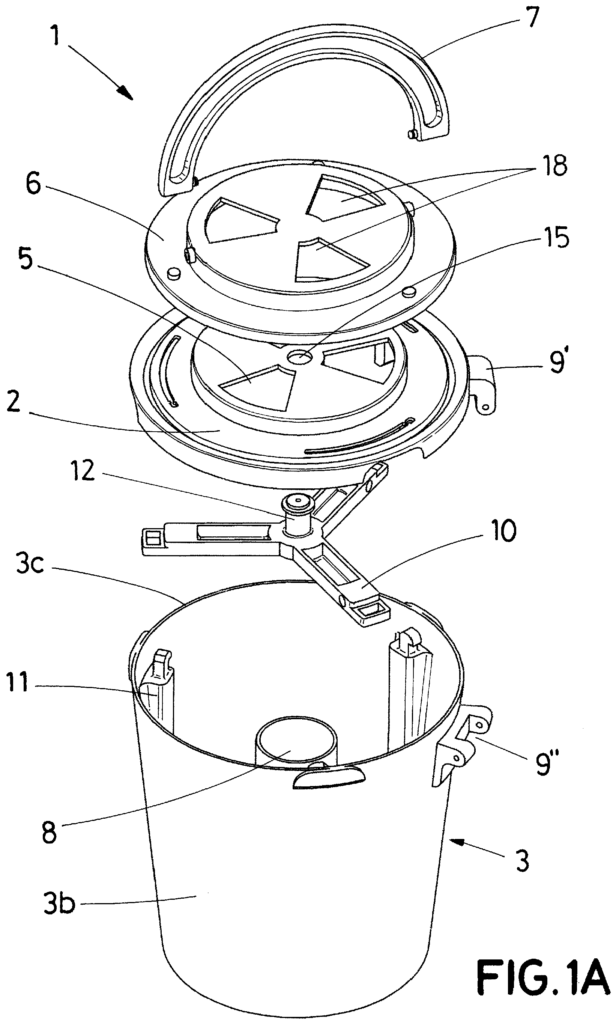
Example of a product model
Below are some examples of prototype mockups. The manufacture of prototype mockups has been carried out using 3D printing techniques and commercially available components. With these mockups, the client has been able to validate the ergonomics of the product as well as the expectation it is capable of generating in its future customers. It is important to note that in the stage of manufacturing prototype mockups, it is still too early to patent the idea.
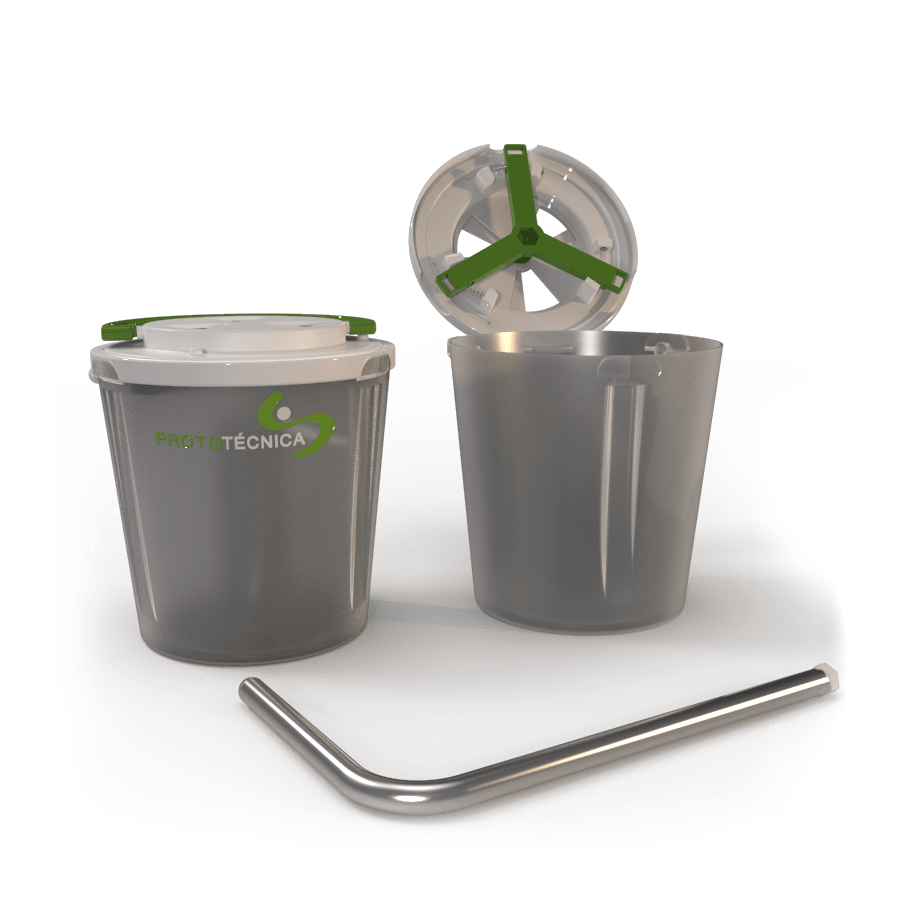

Prototype Type 6: Functional Prototypes Close to Industry
El your working prototype incluye los sistemas y subsistemas que permiten la funcionalidad del prototipo.
Con el your working prototype el cliente inventor puede demostrar ante los inversores y potenciales clientes que el invento funciona, pero aun no pueden definirse los futuros precios de un producto innovador.
El your working prototype ya aporta información suficiente sobre la ergonomía del producto en su propio uso. Además permite proceder con la descripción de la memoria de una patente para proteger las reivindicaciones de innovación del producto innovador.
Es muy importante fabricar un prototipo funcional en procesos anteriores a la presentación de la patente, sobre todo, porque en la fábrica de inventos se consiguen mejoras para abaratar la futura fabricación industrial del prototipo, mejorar la ergonomía de un producto y analizar el comportamiento del mercado al interactuar con el prototipo funcional.
Los precios de un prototipo funcional estará determinado por variables lejanas a los materiales necesarios para construirlo.
Objectives of the Functional Prototype
The objective of a functional prototype is to demonstrate the technical feasibility of an invention. The functional prototype allows for assessing the ergonomics of using a product, as well as the general reaction of potential customers to a product. The objective of a functional prototype is not to make money by selling </span
At Let’s Prototype, we have manufactured over 200 functional prototypes in recent years. We encourage you to check out some of the most outstanding ones.


Prototype Type 7: Pre-industrial Prototypes
Definition of Pre-Industrial Prototype
The pre-industrial prototype is a very advanced version of a product. It is impossible to manufacture a pre-industrial prototype before going through the prototype stages previously described. The prototype creation cycle or product creation process cannot be seen as a linear process. The cycle of creating an innovative product is a continuous learning process that allows validation of the ergonomics of the product as well as the real usability of the prototype's functions.</span
Once enough has been learned from the previous prototype versions, the pre-industrial prototype can be manufactured. This prototype allows for the analysis of different techniques available for industrializing the prototype, that is, mass-producing a product. With this analysis of industrial methods, the pre-industrial prototype is configured. At this point, the steps to manufacture the product as well as the manufacturing costs of an innovative product can be determined.
Objectives of Pre-Industrial Prototype
The main objectives of a pre-industrial prototype are:
- Determine the industrial manufacturing costs of the product.
- Learn about the acceptance of the functional prototype.
- Determine the documentation required for mass production of a product.
In the pre-industrial prototype manufacturing process, the prototype documentation must be prepared. The prototype documentation is the Blueprint for manufacturing the product, it is a detailed list that provides all the components that make up the prototype as well as the notebook of blueprints of the prototype parts and pieces. With this information, an exploration is made in the industry of the different industrial methods for manufacturing a product as well as the possible suppliers necessary for manufacturing. The prototype documentation is essential for preparing the business plan, as with this information, the product prices after mass production can be determined.
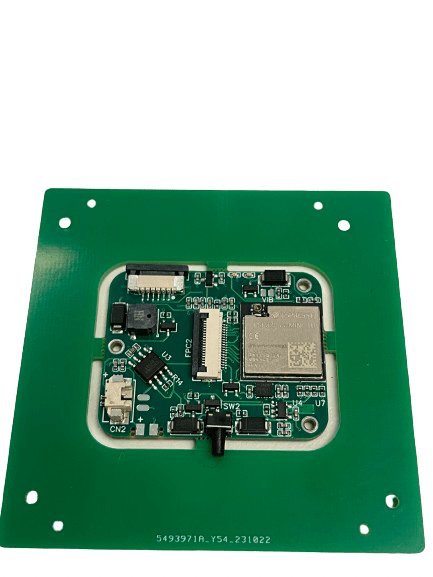
Example of Pre-Industrial Prototype
At Let's Prototype, we have developed several pre-industrial prototypes. Below are images of an innovative product for the tobacco industry.
Most smokers or collectors of Habanos cigars are very concerned about the relative humidity inside their Habanos cigar containers. Relative humidity conditions their preservation, hence the importance of making decisions to maintain relative humidity within appropriate parameters.
At Let's Prototype, a pre-industrial prototype has been developed consisting of an IOT device capable of connecting to the user's mobile phone, where the parameters of acceptable relative humidity for the proper preservation of Habanos cigars are configured. The IOT device can remain in energy-saving mode for many hours, waking up and taking a daily reading to ensure that the environment is in the appropriate preservation conditions. If not, the IOT device sends an alert signal to the user's mobile phone, indicating the incorrect measurement taken and providing some recommendations to ensure an adequate environment inside the humidor.
After manufacturing several prototypes, a pre-industrial prototype has been developed consisting of electronic elements and an ergonomic product design that is small enough to not affect the capacity of the Habanos cigar preservation humidors.
Currently, using prototype manufacturing techniques, a IOT prototype ready for mass production has been achieved. In this case, the pre-industrial prototype itself is already available for sale on major platforms, such as Amazon, which is a very suitable environment for measuring the reaction and acceptance of the prototype by customers.

Other types of product prototypes
Do you want to turn your idea into a product?
The time to bring your ideas to life is now. We accompany you throughout the entire process: from idea to product.
San Juan Ingenieros, S. L, is the owner of the domain www.letsprototype.com, and in accordance with the General Data Protection Regulation (EU 1679/2016), we will process your data exclusively to handle your information request. You have the right to rectify or request the deletion of your data at any time via hello@letsprototype.com.
Valorar este page