Pesticide Innovation Prototypes: There are six motivations to focus on innovating agricultural prototypes that minimize or allow for the replacement of pesticide use. Consumer health protection, environmental protection, pest resistance, soil quality, process economy, and food security are the main elements affected or benefited by innovation related to pesticide use.
Precision Agriculture Prototypes: Precision agriculture involves the optimization of resources, time, and effort needed to tend to a crop across its entire extent. The principle of precision agriculture is the knowledge of precise data for specific areas. Precision agriculture prototypes allow for interpreting and detecting the needs of each area, identifying them, and assigning perfectly dosed specific resources to those areas. Innovative precision agriculture products optimize necessary economic resources and maximize crop profitability.
Blockchain Agricultural Prototypes: When we talk about blockchain, we think of Bitcoin and other virtual currencies. The truth is that blockchain is a horizontal technology, useful in many industries, especially when it is necessary to decentralize the possibility of auditing, ensuring that audited data is not corrupt. Blockchain prototypes for agriculture enable efficient traceability analysis, practically from the field to the consumer's table.
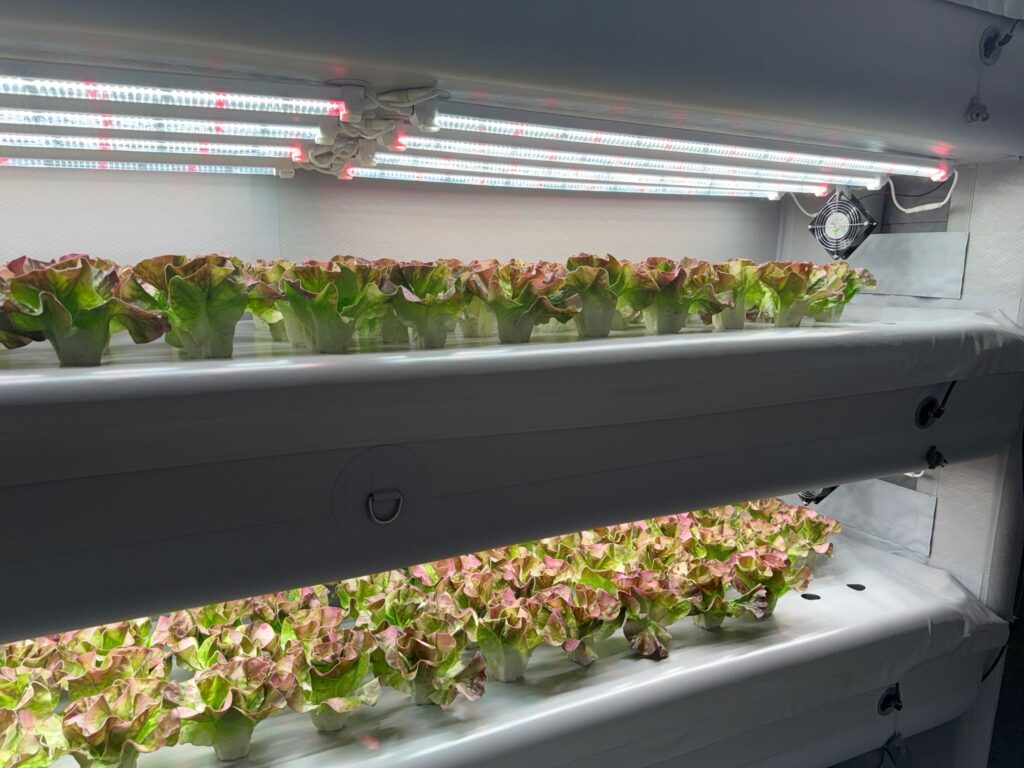
Vertical Agriculture Prototypes: The growing need for agricultural products due to the concentration of society in major cities makes it essential to optimize the space used for urban agriculture. This motivation has been key in the development of technologies and prototypes to improve vertical farming techniques. Within vertical agriculture, two types of agricultural prototypes stand out: Hydroponics and Aeroponics, whose definitions are included later.
AI Agricultural Prototypes: Applying artificial intelligence to agricultural prototypes can yield clear benefits, as long as the prototypes have the capacity to learn and predict. In most cases or examples of AI agricultural prototypes where we have had the opportunity to participate, the goal was:
- Predict weather behavior based on historical data. This way, the amount of nutrients and water resources needed for the crop is conditioned.
- Predict the irrigation needs of the crop based on glucose variations in the plants, considering the historical data of each type of crop.
- Customize water dispensing capacity and logic based on climatic data and soil conditions at each point.
- Dispense nutrients in the water accumulation tank for irrigation, based on color variations at the bases of the plants in different parts of the crop.
All these examples of agricultural prototypes highlight the impact of AI on the development of prototypes useful for the development of precision agriculture.
Robotics Agricultural Prototypes: The development of prototypes with electromechanical solutions and robotics has allowed for the optimization of complex and labor-intensive processes with agricultural prototypes that substantially reduce the time, effort, and costs associated with such agricultural procedures. Robotics prototypes for agriculture make a lot of sense in repetitive tasks, such as harvesting and cleaning procedures of cultivated areas.
Clean Energy Agricultural Prototypes: The optimization of renewable energies, also known as clean energy, is mainly limited by exposure times to natural conditions. Therefore, what poses a limitation in large cities makes perfect sense in energy supply systems for useful agricultural prototypes. At Let’s Prototype, we use this type of energy supply system to power agro-climatic stations and other agricultural prototypes that require electronic elements at different points in the plantations.
7 Steps to Create a Prototype for Agriculture, Agricultural Machinery, or Tools
Definition of the problem.
It is essential to develop a research method that allows, through observation, the quantification of the economic impact of the problem. Many times, inventors create solutions for problems that are not as serious, and this is one of the main causes of prototype failure.
Analysis of innovation trends.
It is essential to understand the innovation trends in agriculture, the latest prototypes in testing phases, and to identify solutions that represent direct or substitute competition for the problem you aim to solve.
Identification of alternative solutions and state of the art.
The analysis of agricultural prototypes can be carried out in two ways. The first is through the patent analysis of agricultural products. For example, if you want to patent in Spain, you can access the OEPM records and find similar solutions using practical methods to conduct a prior art search. In the case of patent registration in the United States, it is even easier to locate patents of similar products to an invention. The USPTO system allows filtering by industry, dates, and the state from where the patent is being filed in the USA. Using these filters, it is essential to understand the inventions that have been patented to solve similar problems. This is especially important because inventors often feel confident innovating new inventions just because they have not found them as commercial products in the market. However, this does not mean they can be patented, since even if a product is not available for purchase, other inventors may have already patented a similar system earlier.
Basic engineering project and technical feasibility of Agrotech systems.
The agricultural engineering projects allow demonstrating the technical feasibility of inventions at a laboratory level. This R&D cycle helps reduce future risks associated with creating inventions that do not yet exist. Before starting any prototype manufacturing process for agriculture, it is essential to prove its technical feasibility and create a kind of prototype manufacturing manual before moving into each stage. Even if substantial changes later arise in the agriculture prototype, the reality is that the prototype development cycle will be much cheaper if it has already undergone enough time and analysis to ensure its technical feasibility.
Manufacturing of the functional prototype for agriculture.
The agricultural prototypes are experimental products that make it possible to learn about the invention manufacturing process. The functional prototype development cycle, in addition to practically validating the technical feasibility of the invention, is a fundamental tool to raise funding for the development of an innovative product. Skipping the functional prototype manufacturing stage represents a very high risk, as it is very likely that the product cannot be mass-produced without first going through an experimental manufacturing process that allows for changes and improvements to be made easily and cost-effectively.
Practical testing of the prototype or agricultural machine in the field
The agricultural prototypes face certain challenges when being tested in the field. Issues with data transmission coverage, as well as limited access to testing environments that simulate or resemble the scenarios where the prototype will ultimately be used, are some of the main barriers inventors must overcome.
Commercialization of the innovative product.
After carrying out functional tests that demonstrate the agriculture prototype is technically feasible and capable of solving real problems found in the field, another equally important challenge arises: proving its economic viability. In this regard, conducting commercial experiments is the best solution, even before starting any series manufacturing cycle.
What is vertical farming? Prototypes for vertical farming.
Vertical farming systems are those in which crops are grown at different heights, allowing for better use of space and improved control over crop conditions. The closest analogy to understand what vertical farming is would be the comparison between single-family homes and apartment buildings.
Types of vertical farming systems.
Definition of Hydroponics
The hydroponics system is a sustainable vertical farming method, consisting of a column or similar structure capable of holding plants in support compartments. These compartments or support rings allow the roots to remain exposed in an environment where the necessary nutrients flow for the controlled growth of the plants.
Definition of Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a vertical farming system very similar to Hydroponics. The main difference between these vertical farming systems is that in hydroponics, nutrients are added based on the control of parameters or nutrients in the water tank. In the case of Aquaponics, the nutrient balance depends on the waste produced by the fish that coexist within the innovative vertical farming system.
Definition of Aeroponics
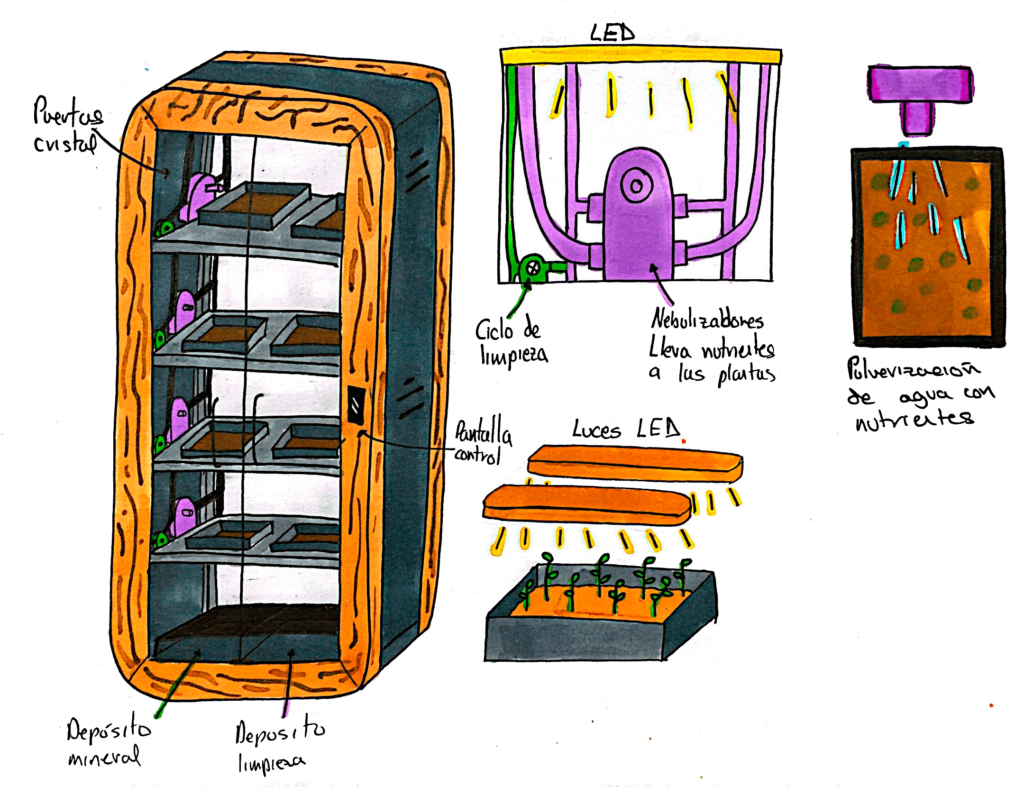
The aeroponics system, unlike the more well-known and popular vertical farming systems such as Aquaponics and Hydroponics, is based on a sealed structure equipped with sufficient electronic components to continuously measure nutrient levels, light spectra, and other critical parameters for plant growth. In aeroponics systems, plants grow on trays without soil, fully exposed, receiving from the environment the necessary nutrients for their growth. There are clear combinations of artificial intelligence, application development, and mathematical models within aeroponics systems, as it is very practical to maintain control by zones, types of crops, updated plantation status, and nutrient loads or light spectrum adjustments remotely.
Best vertical farming systems. Differences and similarities.
| | Hydroponics | Aquaponics | Aeroponics |
Nutrient acquisition | Dissolved in water. | Aqueous solution derived from fish waste. | Nutrients dispensed in the form of mist. |
Nutrient control | Continuous nutrient monitoring in the tank | Continuous control of the balance between fish and plants. | Nutrient control in the hermetic space of the cabinet. |
Sustainability | Media. Requires addition of non-natural clients. | High. Relies on a natural biological cycle. No external artificial nutrients are added. | Medium. Requires addition of non-natural nutrients. |
Advantages | Accurate control of plant growth | Precise control of plant growth and fish evolution. | Accurate control of plant growth |
Development costs | Middle | Middle | High |
Technical complexity | Middle | Middle | High |